Can A Bad Alternator Cause Transmission Problems?
Has your car been experiencing transmission problems? Are you also noticing issues with your electrical system, such as dashboard light or engine light? It may surprise you, BUT a bad alternator could be the culprit behind both of these issues.
Wait, can a bad alternator cause transmission problems while alternator and transmission are two separate components in a car?
Yes, a bad alternator can cause transmission problems if the car has an automatic transmission with electronic circuitry. This can lead to a voltage drop, affecting the transmission servos and torque converter, ultimately causing malfunctioning transmission gears, rough shifts, and stalling problems.
In this blog, we will explore how a bad alternator cause transmission problems, common symptoms of a failing alternator, and how to address these issues to keep your car running smoothly.
What Is an Alternator, and How Does It Work?
The alternator plays the role of an electrical power generator in your car’s electrical system. It primarily consists of three key components: the rotor, stator, and voltage regulator. As the engine runs, a belt connected to the crankshaft drives the alternator’s rotor, inducing a magnetic field.
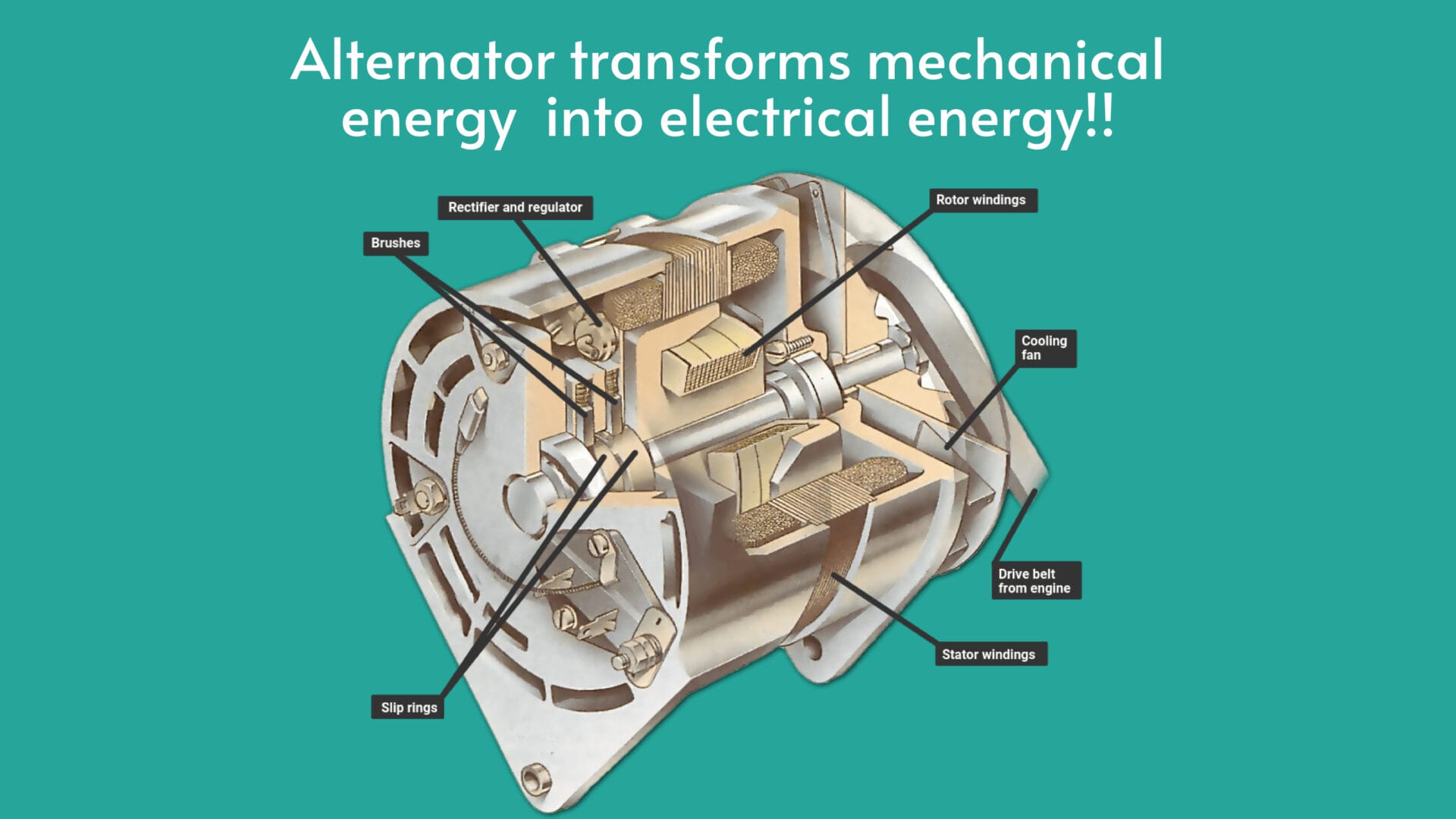
The rotor, essentially a coil of wire wrapped around an iron core, spins within the stator, which is a stationary set of coils. This rotation generates a changing magnetic field, leading to the production of alternating current (AC) in the stator windings.
However, vehicles rely on direct current (DC), so the alternator’s voltage regulator steps in to convert the AC into DC. The regulator ensures a steady output of around 14 volts, charging the battery and powering various electrical components.
To prevent electrical issue, modern cars alternator mostly equipped with diodes that convert AC to DC more efficiently. These diodes act as one-way valves, allowing the flow of electricity only in the desired direction.
In essence, the alternator transforms mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, supplying power to your car’s lights, radio, and other electronic systems while keeping the battery charged. It’s a finely tuned symphony of magnetic fields and electrical currents that keeps your vehicle running smoothly.
What Happens When Alternator Goes Bad
When an alternator in a car goes bad, it sets off a chain reaction of electrical woes that can significantly impact performance.
As the alternator deteriorates, the first signs may include dimming headlights and dashboard lights. This indicates a faltering charging system. The alternator’s rotor may wear out, affecting its ability to generate a magnetic field within the stator.

The voltage regulator, responsible for maintaining a stable electrical output, may also fail and cause erratic voltage levels (low charging below 10.5 or overcharging above 15 VDC). This can result in all kinds of intermittent electrical control module malfunctions, such as transmission, navigation, SRS/airbag, traction/ABS, sensor malfunctions, ECM, lighting, video, audio, and so on.
As the alternator struggles to provide a consistent power supply, the battery takes a hit. A failing alternator cannot effectively recharge the battery, leading to constant depletion. This manifests as difficulty starting the car, frequent jump starts, or a need for repeated battery replacements.
Beyond the immediate electrical issues, the lack of power can also affect critical systems. For instance, the fuel injection system may suffer, leading to poor engine performance (belt-driven) and reduced fuel efficiency. The alternator’s struggle to meet electrical demands also affects electronic components such as power windows and air conditioning, rendering them unreliable.
Moreover, modern alternators have diodes that convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). A malfunctioning diode can cause electrical feedback and fail to convert AC to DC properly. This can potentially damage other components in the vehicle, like ECU, sensors, and even your battery.
In essence, a bad alternator jeopardizes the entire electrical ecosystem of the car, affecting everything from ignition to the overall driving experience.
Can a bad alternator cause transmission problems?
Yes, a bad alternator can cause transmission problems due to erratic voltage output (below 10.5 or above 15 volts). When a faulty alternator causes electrical issues and affects the car’s voltage regulators, it can result in low voltage output, impacting the transmission system. Due to this voltage issue, transmission electronic operators, including overdrives, certain gear splitters, and dual-clutch may stop working and cause the transmission to go into limp mode.
This can also affect the transmission servos and torque converter, ultimately causing malfunctioning transmission gears.
How?
Since 1993, most general motor vehicles have been electronically controlled. These electronic systems depend on accurate and stable electrical signals to manage their various functions.
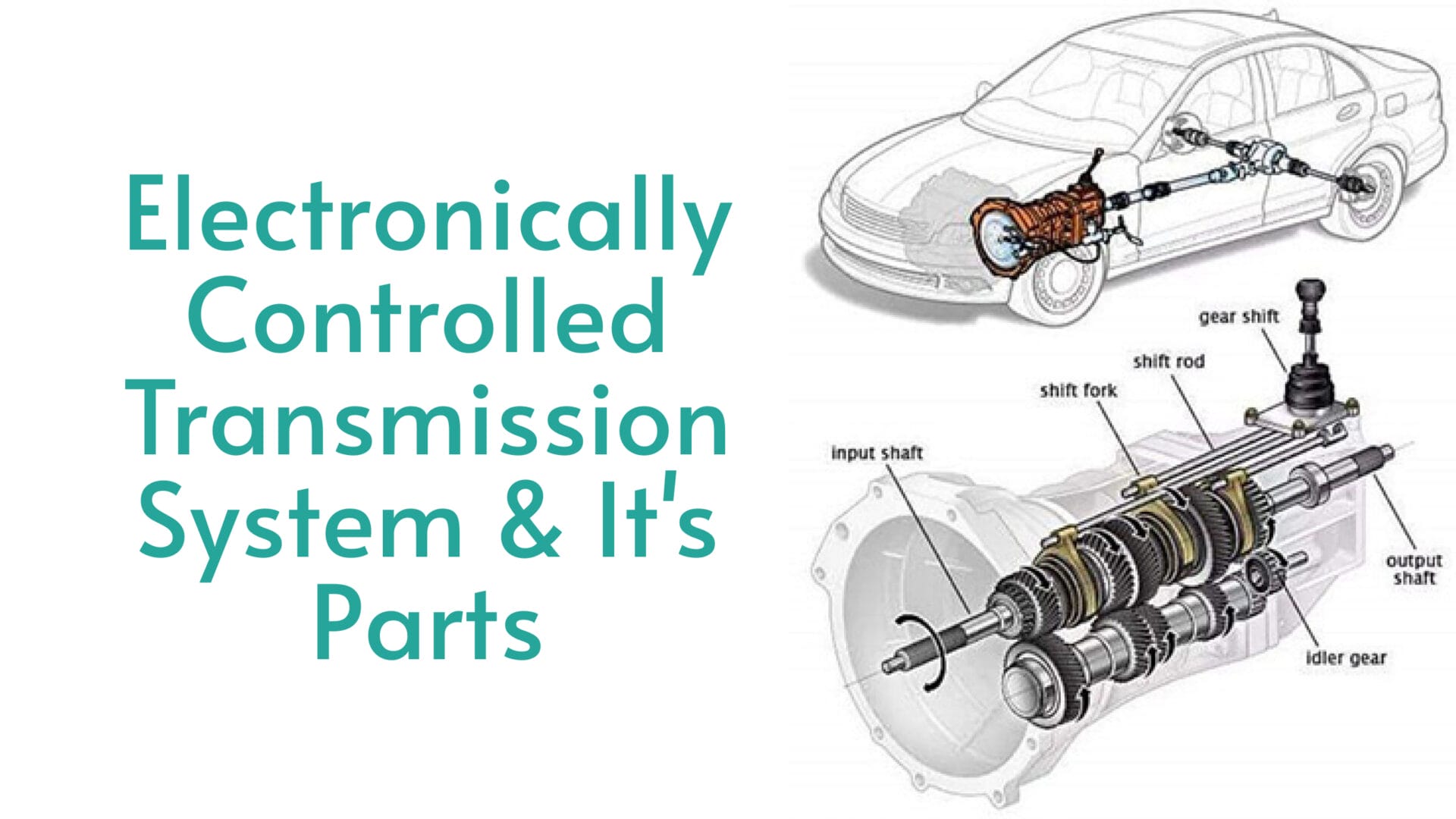
And modern cars are super high-tech. If there’s insufficient voltage, particularly from the alternator, ECM can throw a bitch fit and result in misinterpretations or delays in these crucial signals. This disruption in electrical communication within the transmission can lead to issues like delayed or rough shifting, inconsistent performance, and the risk of long-term damage to transmission components.
Transmission Problems A Bad Alternator Can Cause
A failing alternator can have a negative impact on the transmission. This can result in transmission shifting problems, such as delays in gear changes, harsh shifts, or unexpected slipping out of gear. Let’s know what transmission problems a bad alternator can cause and how.
Transmission Shifting Issues:
Voltage irregularities from a bad alternator disrupt precise electronic signals in the transmission, causing delayed or rough shifting.
Sensor Malfunctions:
Unstable voltage can interfere with transmission sensors to measure speed, temperature, and fluid levels. This will result in inaccurate data for the transmission control module.
Issues with the Control Module:
Disrupted signals make it challenging to Handle the transmission precisely. This may show up as irregular shifting patterns or improper engagement of the gears.
Premature Wear and Tear:
Voltage irregularities stress transmission components, contributing to premature wear and potential damage. This will increase maintenance costs and shorten the transmission system’s lifespan
Reduced Fuel Efficiency:
Transmission issues from alternator problems can reduce fuel efficiency due to inefficient shifting and increased strain on the engine.
How To Identify A Bad Alternator
Dim or flickering dashboard lights are often indicative of a failing alternator, while whining or whirring noise from the engine could also signal a bad alternator. Despite a fully charged battery, low voltage may cause headlights to dim. Additionally, a failing alternator can lead to electrical system malfunctions and result in rough shifts or car stalling. Let’s know in detail.

Dimming Lights:
A noticeable dimming of headlights and interior lights, especially at idle or low speeds, suggests a potential alternator issue.
Strange Noises:
Unusual noises, such as grinding or whirring, may indicate worn-out bearings inside the alternator, signaling an impending failure.
Warning Lights on the Dashboard:
The illumination of the alternator warning light on your dashboard is a clear signal that the charging system is encountering problems.
Dead Battery:
If your battery is showing a battery warning light, it is frequently dead or struggles to hold a charge. It may be a consequence of an alternator failure or inability to recharge it adequately.
Electrical Glitches:
Malfunctions in various electrical components, such as power windows or the radio, can indicate an alternator struggling to provide consistent power.
Burning Smell:
A burning odor, especially when using electrical components, may suggest overheating within the alternator due to internal issues.
Difficulty Starting the Car:
A struggling or delayed start, despite a functional battery, may be a result of the alternator’s inability to provide sufficient power to kickstart the engine.
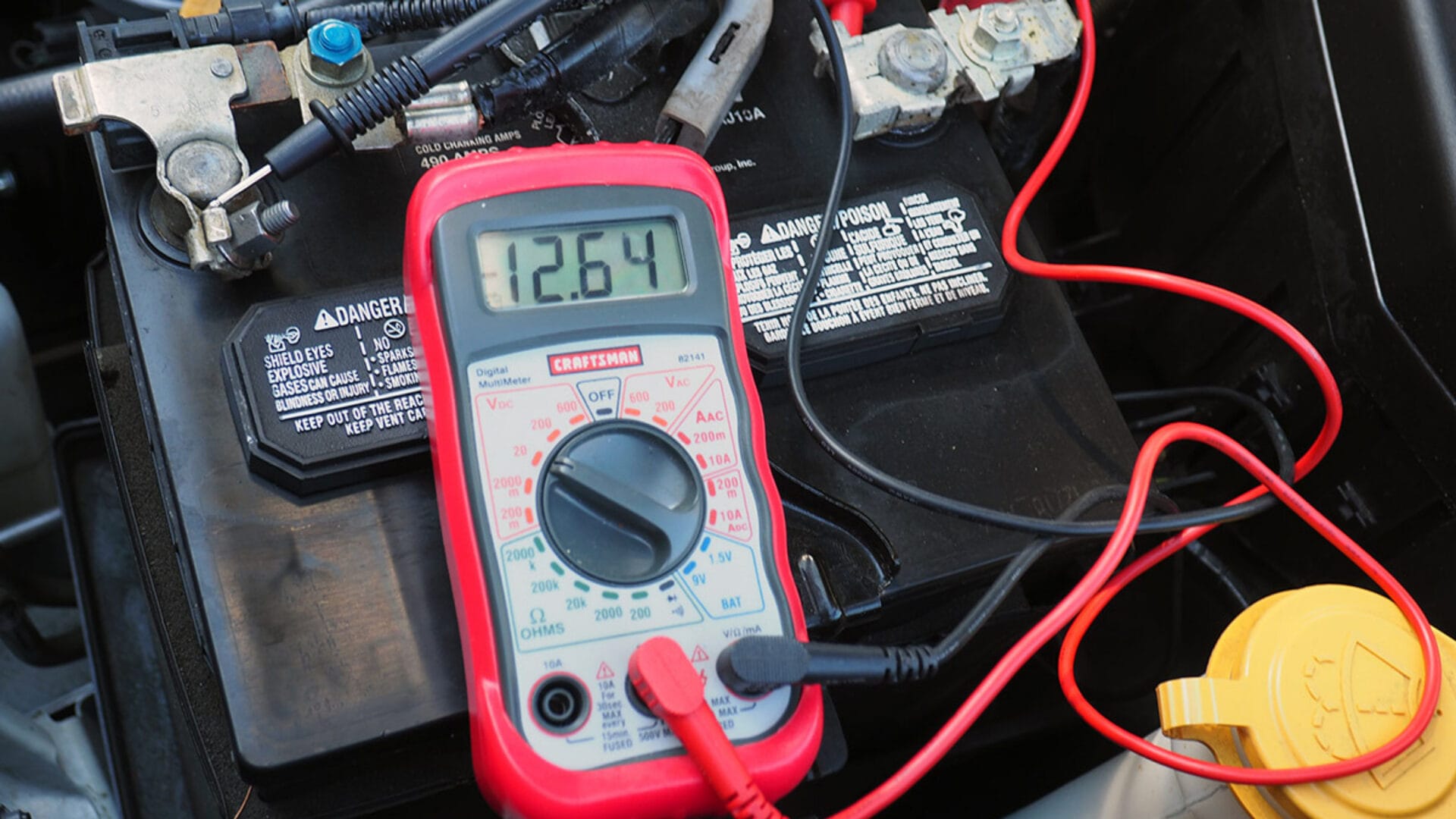
Dashboard Voltage Reading:
Use a voltmeter to check the voltage across the battery terminals. A reading below 13.5 volts while the engine is running may signal alternator problems.
Timely attention to alternator issues can save car enthusiasts from the headache of extensive repairs and unexpected breakdowns on the open road. So, if you notice any of these signs, don’t wait; give your trusted mechanic a call and ensure the continued reliability of your vehicle’s electrical system.
How To Fix Bad Alternator?
To identify the cause of a bad alternator, check voltage output and continuity with a voltmeter. Ideally, it should fall between 13.5 and 14.5 volts; deviations from this range may indicate a problem. If voltage output consistently falls below the recommended range of 10.5 volts, consider replacing the alternator to restore proper charging functionality.
A weak battery (bad battery) can strain the alternator, leading to premature failure. Regularly assess your battery terminal; if it’s lightly corroded, clean it, and if cleaning is not enough, replace it with a new battery terminal. Corrosion can disrupt electrical flow, and compromise alternator performance, and cause loss of battery power. So do inspections regularly to prevent overworking the alternator.
Belt is another part that can disrupt the alternator’s performance. Check it; not always it will cause a problem only when it’s worn. A new belt can also be the reason if it’s loose. So check it and tighten it, or simply replace it if it has aged or worn out.
Will Fixing It Solve Transmission Problems?
It should. Because alternator doesn’t physically damage any part of the transmission system. Due to its failure transmission operating system is disrupted. If it doesn’t run for a long time—I mean, you have not dragged your car with a bad alternator for a long time—fixing the alternator problem will fix transmission issue as well. Alternator will again provide enough power supply to operate the transmission system efficiently. You won’t need to do transmission repair separately.
Nevertheless, after replacing the alternator, if you still experience a transmission problem that may be related to a defective alternator, you can take the following actions:
- Check the transmission fluid level; if it has drained too much, refill it with the recommended fluid level (1.8–10.3 US quarts for City Car, Family Car, Sedan)
- Then check the sensors and other electronic components. If found damaged and repairable, take it to a mechanic; if not, replace it
- Usually, it doesn’t happen, but if you already have a weak or aged transmission system and it’s further damaged by the bad alternator, you may need to replace the transmission system. But it’s very rare if you have a well-maintained transmission system.
Can A Weak Alternator Cause Poor Engine performance?
Yes, a weak alternator can indeed lead to poor engine performance.
When an alternator is weak, it struggles to provide sufficient electrical power to the engine and other crucial components. This shortfall has an impact on the ignition system, resulting in poorer spark quality and incomplete fuel combustion, which lowers engine power, reduces fuel efficiency, and increases emissions.
Moreover, a weak alternator may fail to adequately power the engine control module (ECM) and other sensors, causing disruptions in the engine management system. This can lead to irregular air-fuel ratio, ignition timing, and other essential parameters, further impacting overall engine performance.
In summary, a weak alternator hampers the engine’s ability to operate at its best, resulting in diminished power, efficiency, and overall drivability.
Can A Bad Car Alternator Cause Acceleration Problems?
Certainly!
A malfunctioning car alternator, particularly if it produces overvoltage or overcharging, can lead to acceleration problems. Excessive voltage, beyond the standard 14 volts, can cause issues such as overheating in the ignition coil, misfiring due to erratic spark timing, and potential damage to the engine control module (ECM). This results in poor engine performance, affecting acceleration.
Testing the alternator involves checking voltage and current output to ensure they meet specifications. Additionally, inspecting battery terminals and lead clamps for cleanliness is essential, as even minor corrosion can impede the alternator’s charging capability. Proper diagnosis is crucial, as acceleration problems may not solely stem from the electrical system, and other factors should be considered.
Can Low Voltage Cause Transmission Problems?
Yes, low voltage can cause transmission problems.
In modern vehicles, electronic components, including sensors and the transmission control module (TCM), depend on a stable electrical supply. Low voltage can disrupt the signals between these components, leading to issues like delayed or rough shifting, erratic behavior, or even failure to engage gears properly. In simple terms, insufficient voltage hampers the smooth operation of the transmission’s electronic systems, causing performance issues.
Regular maintenance, including checking the alternator and electrical components, helps prevent such problems and ensures a smooth driving experience.
Can A Bad Alternator Cause Transmission Problems In A Manual Car?
No, a bad alternator typically does not cause transmission problems in a manual car.

Because, unlike automatic cars, manual cars have transmissions that rely on the mechanical linkage between the clutch and gears, not on electrical systems. So whether the alternator is bad or good, it doesn’t create transmission problems in manual cars.
FAQ
Can an alternator affect the clutch?
In most vehicles, the alternator does not directly affect the clutch. However, some modern cars with advanced electronic systems may have a clutch connected to the ECM or other electronic components. In these cases, if the alternator is malfunctioning and not providing sufficient power, it could indirectly impact the performance of the clutch.
How do I know if my alternator is OK?
You can test your alternator with a voltmeter to know if it is OK or not. Grab a voltmeter, rev your engine to 2000 RPM, keep it running, and test the battery. If your voltage climbs from around 12.2 V to 13-14.5 V, good news – your alternator is rocking!
But if the voltage stays the same or drops, not-so-good news; it might be time to give your alternator a closer look.
How do I know if I need a new alternator?
Keep an eye out for dimming battery light, warning indicators on your dashboard, or strange noises like grinding. If your car battery frequently dies, even when charged, or if you experience electrical glitches like malfunctioning power windows, know that your car needs a new alternator replacement.
A burning smell during electrical use is also a red flag. You can check the battery voltage while the engine’s running; if it consistently falls below 13.5-14.5 volts, your alternator is dead and needs replacement.
Closing Words
The alternator, often underestimated, holds more sway than we realize. Beyond powering our vehicles, it quietly influences the transmission’s performance. It can cause severe transmission problems. From voltage fluctuations to erratic shifting, its influence extends beyond the realm of mere power generation. So give your alternator priority; inspect and maintain it properly in time to avoid such problems.






