Spark at Points But Not at Plugs – Find Out Reason and Troubleshoot
When searching for the cause of poor engine performance or misfires, the phrase “Spark at points but not at plugs” is frequently used to describe a typical problem in car ignition systems in which sparks are created at ignition points but fail to reach the spark plugs.
Since it affects vehicle performance, safety, and expenses, understanding the issue is crucial for vehicle owners.
Immediate attention to ignition issues can save money on fuel, avoid costly repairs, and boost dependability. By lowering emissions, it helps with environmental sustainability as well. With an understanding of this issue, you can protect your vehicles’ performance, longevity, and resale value.
In this guide, the causes of this issue and potential solutions will be explored thoroughly so you can have a crystal-clear understanding.
- Ignition System and How it Contributes to The Problem
- Common Causes of Sparks at Points but Not at Plugs
- Comprehensive Ignition System Troubleshooting Guide: Addressing Sparks at Points, Not at Plugs
- Understanding Spark Plug Gap and Correct Installation: Optimizing Engine Performance
- How to Prevent Spark Problems?
Ignition System and How it Contributes to The Problem
The ignition system of the vehicle uses the spark plugs to produce an electric spark, which starts the combustion process. A severe ignition system fault occurs when sparks travel elsewhere than the spark plugs. The ignition system generates sparks at spark plugs to ignite the engine cylinders’ air-fuel mixture. Unintended sparks affect combustion timing and distribution.
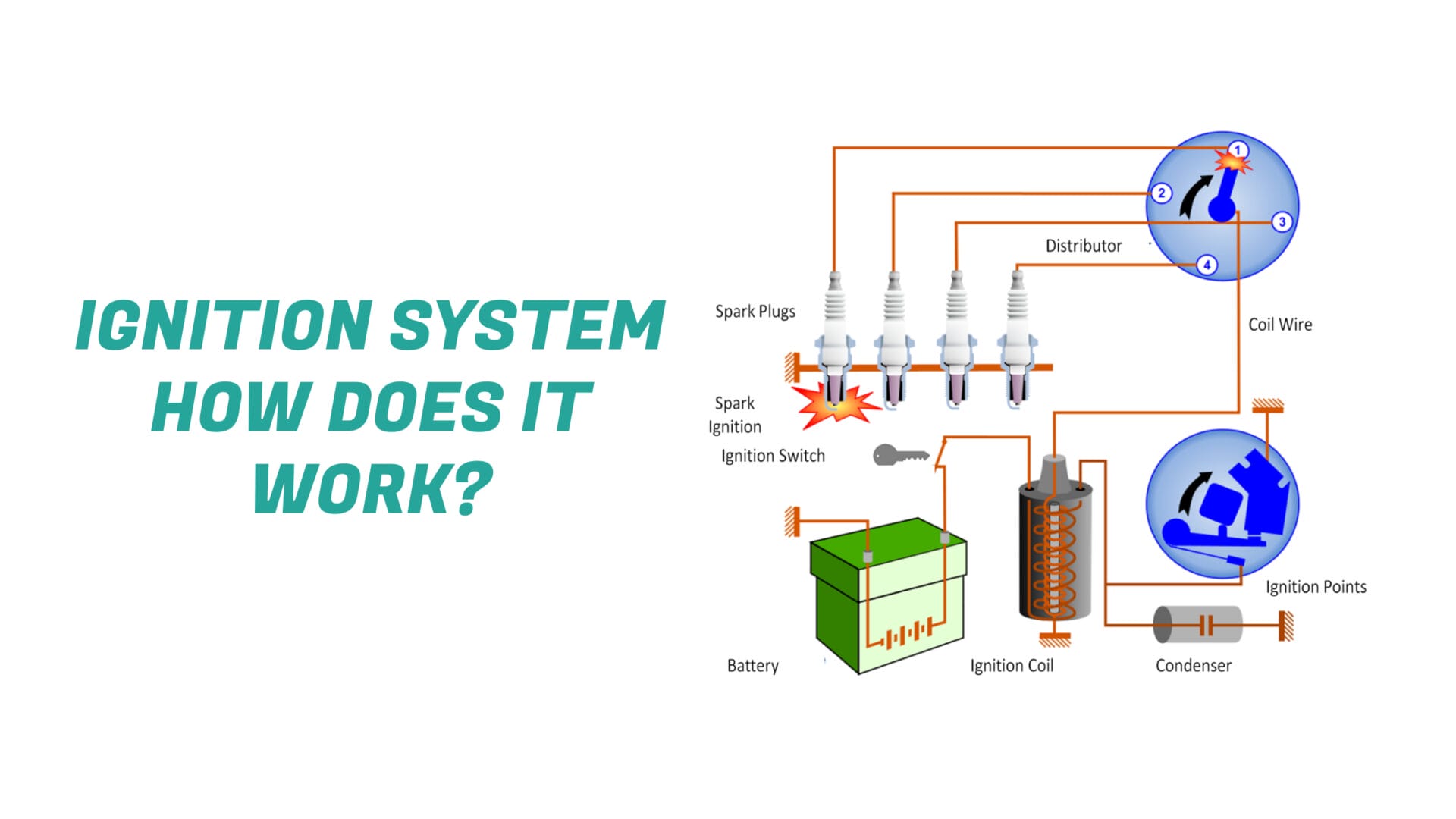
To maximize combustion efficiency, engine ignition is timed to happen at certain moments in the four-stroke cycle. To avoid problems like misfires, it is crucial to distribute the spark properly so that all of the cylinders receive an equal amount of fuel and air. For troubleshooting and diagnosis, familiarity with the ignition system is fundamental while working on an engine.
Common Causes of Sparks at Points but Not at Plugs
Sparks occur at points not at plugs due to various causes.
1. Ignition Coil Issues: Malfunctioning ignition coils can cause erratic spark distribution, leading to ignition coil issues.
2. Carbon Tracking: Carbon deposits on the distributor cap or spark plug wires can create unintended paths for sparks, which track carbon.
3. Incorrect Spark Plug Gap: Improper gap settings on spark plugs can cause sparks to occur at undesired locations.
4. Worn-out Rotor or Distributor Shaft: The wear and tear on the rotor or distributor shaft can disrupt the intended spark path.
5. Crossfiring: Crossfiring between spark plug wires can cause sparks to occur at unintended points.
To fix the issues, replace faulty ignition coils, clean or replace carbon-tracked components, adjust spark plug gaps, and inspect or replace worn-out rotor or distributor shaft. Ensure you properly route the spark plug wires to prevent cross-firing.
Comprehensive Ignition System Troubleshooting Guide: Addressing Sparks at Points, Not at Plugs
Follow these detailed steps to troubleshoot and replace each component of the ignition system. Always exercise caution, and if you are unsure, seek professional assistance.
- Inspect the spark plug wires:
- Disconnect the car battery’s negative terminal.
- Pull at the boot to carefully remove the damaged spark plug wire.
- Follow the existing routing to place the new wire and ensure a secure connection at both ends.
- Reconnect the battery terminal.
- Examine the distributor cap:
Cleaning Procedure-
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal during the cleaning procedure.
- Carefully remove the distributor cap.
- Mix baking soda and water to clean the interior of the cap.
- Wipe dry, and make sure you remove any residue.
- Reinstall the cap and reconnect the battery terminal.
Replacement Procedure-
- After cleaning, inspect the cap for cracks.
- If cracks are present, replace it by removing it and securing the new one in place.
- Check the ignition coil:
Reading Indicating Malfunction-
- Use a multimeter in resistance mode.
- A reading of infinite resistance or significantly lower than specified indicates a faulty ignition coil.
Replacement Procedure:
- Disconnect the battery.
- Remove the electrical connectors and mounting bolts securing the ignition coil.
- Install the new coil and reconnect the wires.
- Inspect the spark plug gap:
Adjustment Procedure-
- Measure the gap using a spark plug gap tool.
- Carefully bend the ground electrode if adjustments are necessary.
Replacement Procedure-
- To replace the old spark plug, use a spark plug socket to unscrew it.
- Hand screw in the new spark plug, then use a wrench to tighten it.
- Examine the Rotor and Distributor Shaft:
Inspection Procedure-
- Remove the distributor cap.
- Check the rotor for wear or damage.
- Inspect the distributor shaft for any abnormalities.
Replacement Procedure:
- If wear or damage is detected, remove the old rotor.
- Install the new rotor, ensuring proper alignment.
6. Track carbon emissions:
Cleaning Procedure-
- To clean, remove the distributor cap.
- Clean up any visible carbon deposits with a clean cloth.
- Replace the cap if it is significant.
7. Verify wire routing:
Adjustment Procedure-
- Trace the existing routing of spark plug wires.
- Ensure you adequately separate the wires and avoid any contact or interference.
- Make sure to adjust the routing as necessary to prevent cross-firing.
Understanding Spark Plug Gap and Correct Installation: Optimizing Engine Performance

You need to determine the power and timing of the spark in your engine by measuring the distance between the center and ground electrodes, which is known as the spark plug gap. Misfires, weak sparks, and overall engine underperformance can result from incorrect gaps.
To change spark plugs, follow these instructions:
- Gather a spark plug socket, extension, and ratchet.
- Disconnect the coil-on-plug connectors or spark plug wires.
- Remove old spark plugs using the appropriate socket.
- Use a feeler gauge to check the gap for accurate spacing.
- Thread the new spark plugs into the cylinder head by hand to avoid cross-threading.
- Use a torque wrench to tighten the spark plugs to the recommended torque.
- Reconnect the spark plug wires or coil-on-plug connectors.
Addressing sparks at points, not at plugs, crucially involves changing spark plugs. Changing the spark plugs can often resolve issues such as misfires, weak sparks, or an underperforming engine if you have been experiencing them. Optimize your engine’s performance by ensuring the correct gap and following proper installation procedures.

How to Prevent Spark Problems?
Here’s some tips on how you can eliminate all the potential spark issues-
Routine Upkeep Procedures
It is essential to do maintenance on your car following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Spark plugs should be checked and replaced at regular intervals and other parts of the ignition system and the engine should be tuned up as well.
The Effect of Fuel Quality on Ignition
It’s crucial to use premium fuel with the correct octane level. Carbon accumulation on spark plugs is a sign of low-quality fuel that might hinder combustion.
The Value of Clean Air Filters
Maintaining a clean air filter guarantees an optimal air-to-fuel ratio during combustion. The air filter should be checked and replaced at the recommended intervals.
Maintenance and Cleaning of Fuel Injectors
Fuel spray patterns and combustion might be negatively impacted by filthy or blocked fuel injectors.
Plus, fuel injectors and by extension the effectiveness of the ignition system, can benefit from periodic cleaning or the use of fuel additives.
Final Thoughts
DIY ignition system repairs are possible, but it’s important to know when expert help is needed. Ask a mechanic for aid if you’re unsure of the diagnosis or lack the skills and knowledge.
Ignition systems are complex and crucial to your vehicle’s performance. Professional assistance can save you time, money and ensure proper resolution. If you have any further queries feel encouraged to let us know!






